How To Find V2 In Combined Gas Law
The Combined Gas Law
Since ![]() , If nosotros change one of the variables, (P, Five, n, or T) so i or more of the other variables must likewise change. This leads to the equation
, If nosotros change one of the variables, (P, Five, n, or T) so i or more of the other variables must likewise change. This leads to the equation ![]() or if the number of moles stays the same
or if the number of moles stays the same ![]() .
.
Boyle's Law:
Boyle'south Police force examines the effect of changing book on Pressure. To isolate these variables, temperature must remain constant. We can eliminate temperature from both sides of the equation and we are left with P1V1= P2V2
![]()
Sample Trouble: A piston with a book of gas of 1.0 m3 at 100 kPa is compressed to a terminal volume of 0.fifty m3. What is the terminal pressure level?
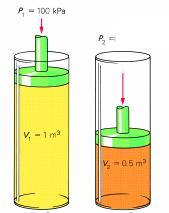
P1 is 100 kPa
V1 is 1.0 miii
Vii is 0.l m3
Ptwo is unknown
PiV1= P2V2 becomesCharles'southward Constabulary
Charles's Law examines the effect of changing temperature on book. To isolate these variables, force per unit area must remain constant.
![]() then Charles's law is
then Charles's law is ![]()
Sample problem: A piston with a volume of gas of 1.0 grandiii at 273 One thousand is cooled to a temperature of 136.five Thou. What is the concluding volume? (Assume pressure is kept constant.)
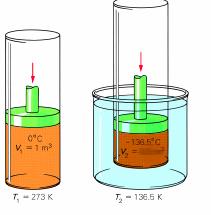
T1 is 273 K
V1 is 1.0 g3
52 is unknown
T2 is 136.v K
The solution becomes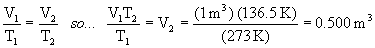
Charles law Applet See what happens when y'all increase temperature. Increasing temperature __________ pressure.
GUY-LUSSAC'S Police
Near the turn of the 19th century, Guy-Lussac investigated the relationship betwixt pressure level and temperature while the volume was held abiding. When the temperature goes up the pressure inside a rigid container also goes upwardly. For example, your car tires, when inflated, are essentially rigid, the volume volition not change. Did you notice that when the temperature goes up the force per unit area inside your tires also increases?
We tin again use the combined gas law to quantify this relationship.
Sample Problem: If your tire is 2 liters and the initial pressure is two atm, what is the final pressure when the temperature goes from 0 degrees celcius (273 K) to 100 degrees celcius (373 K)?
T1 is 273 Chiliad
P1 is 2 atm
Ptwo is unknown
T2 is 373 K
First, start with the combined gas law and cancel out the volumes because they do not modify.
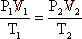
Subsequently removing the volumes,
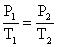
Rearranging the equation: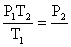 so the terminal pressure P2, is (2.00 atm)(373K)/(273 K) = two.73 atm
so the terminal pressure P2, is (2.00 atm)(373K)/(273 K) = two.73 atm
Source: https://web.fscj.edu/Milczanowski/psc/lect/Ch4/slide12.htm
Posted by: benoithoughle.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Find V2 In Combined Gas Law"
Post a Comment